chest compression test trauma|chest injury physical therapy : supplier METHODS Manuscripts were identified through a search of MEDLINE, . Tudo começou quando o seu melhor amigo, Marshall, lança a bomba de que pedirá a sua namorada de longa data, Lily (uma professora do jardim de infância), em casamento. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
23 de jul. de 2015 · The mining company sues, and Joe — called a half-breed during the disturbance — takes the blame for firing the first to .
A plain chest radiograph (CXR) is obtained for all hemodynamically stable patients who present with blunt chest trauma of any significance or who have any signs or symptoms (eg, chest pain, chest wall tenderness).A prospective analysis of 28-32 versus 36-40 French chest tube size in trauma. AU .
METHODS Manuscripts were identified through a search of MEDLINE, .We compared outcome for the subgroups that had CT or PC placed for a PTX. For .Medline ® Abstract for Reference 89 of 'Initial evaluation and management of .
91 PubMed | TI British Thoracic Society Guideline for pleural disease. AU .{{configCtrl2.metaDescription()}}
Children, young people and adults who have experienced a suspected major chest trauma as follows: tension pneumothorax, haemothorax, cardiac tamponade, pneumothorax, pulmonary .
Overview of testing — A plain chest radiograph (CXR) is obtained for all hemodynamically stable patients who present with penetrating chest trauma, whether or not . Objectives: Identify the signs and symptoms indicating possible hemodynamic compromise in patients with chest trauma. Create a clinically guided diagnostic plan in .
tension pneumothorax chest trauma
continental aircraft engine compression test
Emergency trauma management (see "Initial management of moderate to severe hemorrhage in the adult trauma patient" and "Approach to shock in the adult trauma patient" . Thoracic trauma is broadly categorized by mechanism into blunt or penetrating trauma. The most common cause of blunt chest trauma is motor vehicle collisions (MVC) .
Blunt thoracic trauma is more common than penetrating trauma and represents a significant burden for trauma services. 1 This article provides an overview for clinicians caring for patients .Purpose of review: This article provides an overview of the common and important chest injuries that the anesthesiologist may encounter in patients following trauma including blunt injury, . In blunt thoracic trauma, the National Emergency X-Radiography Utilization Studies (NEXUS) chest decision algorithm suggests any of the following findings warrant subsequent imaging evaluation: patient age greater .
Chest wall findings on the affected side include reduced breath sounds, hyper-resonance to percussion and hyper-expansion. Diagnostic modalities include chest X-ray, . Chest trauma is an important public health problem accounting for a substantial proportion of all trauma admissions and deaths. It directly account for 20–25 % of deaths due to trauma. . (62.8 %) patients were diagnosed as polytrauma cases. At presentation, chest compression test (CCT) was found to be positive in 846 (67.25 %) patients and .
continental compression test
IV. Evaluation: Trauma Exam (Emergency Department) Patient lying supine. Compress iliac crests between examiners two hands; Pelvic Instability on Compression . These images are a random sampling from a Bing search on the term "Pelvic Compression Test." Click on the image (or right click) to open the source website in a new browser window . Anatomic and physiologic changes of pregnancy influence the assessment, management, and prevention of trauma. 3, 6 Physiologic changes include a 30% to 50% increase in blood volume and a 40% to 50 . While the initial screening test in thoracic trauma is the frontal chest radiograph obtained in the trauma bay, in many emergency rooms, this is accompanied by E-FAST (extended focused assessment with sonography in trauma) performed by non-radiologists. . Wedge compression and burst fractures secondary to hyperflexion and axial load . Examination — Signs of rib fractures include point tenderness on a specific rib or focal tenderness caused by compression of the ribcage distant from the site of pain. Bony crepitus and ecchymosis may be present. . Chest radiographs (all patients) — In patients with suspected rib fractures or chest wall trauma, chest radiographs .
Trauma is the leading cause of death among individuals under 40 years of age, and pulmonary trauma is common in high-impact injuries. Unlike most other organs, the lung is elastic and distensible, with a physiologic capacity to withstand significant changes in contour and volume. The most common types of lung parenchymal injury are contusions, lacerations, and .A. A compression injury may only involve mild contusions to the chest and no other trauma. B. A compression injury may involve massive damage to the chest wall but typically no internal injuries. C. In a compression injury, bullets, knives, pieces of metal or glass, steel rods, pipes, and various other objects can penetrate the chest wall. D. A .
The American Red Cross CPR guidelines recommend 100 to 120 chest compressions per minute, 30 at a time. Remember these five points: Hand position: Two hands centered on the chest; Body position: Shoulders directly over hands; elbows locked; Compression depth: At least 2 inches; Rate of compressions: 100 to 120 per minuteHypoxia is the most important feature of chest injury. Early interventions should attempt to ensure that an adequate amount of oxygen is delivered to the portions of the lung capable of normal ventilation and perfusion. Abnormalities in circulation can be caused by blood loss, increased intrapleural pressure, blood in the pericardial sac .The LUCAS device is an easy-to-use mechanical chest compression device that helps lifesaving teams around the world deliver high-quality, guidelines-consistent chest compressions to sudden cardiac arrest patients; in the field, on the move and in the hospital. Previous. Next. Strengthening the chain of survival
Background. Cardiac arrest is a severe, life-threatening condition and remains a leading cause of out-of-hospital death worldwide. Adult patients who experience out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) have a low survival rate, approximately 10.4%, and only 8.2% of them survive and have a good functional status [].Standard cardiopulmonary resuscitation (STD .A. A mechanism of injury involving a compression injury could be a driver striking his chest on a steering column. B. A compression injury may involve massive damage to the chest wall but typically no internal injuries. C. A compression injury may only involve mild contusions to the chest and no other trauma. D. In a compression injury, bullets . Examining the evidence on closed chest compressions for traumatic cardiac arrest looking at a paper from Resuscitation . The Applied Knowledge Test (MCQ/SBA) Chapter 2 – The MLA Clinical and Professional Skills Assessment . animals underwent captive bolt injury to the right thigh and controlled haemorrhage (30% blood volume). Sixty . Introduction This study was designed to compare the outcomes of standard cardiopulmonary resuscitation (STD-CPR) and combined chest compression and abdominal compression–decompression cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CO-CPR) with a new device following out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). Moreover, we investigated whether patient .
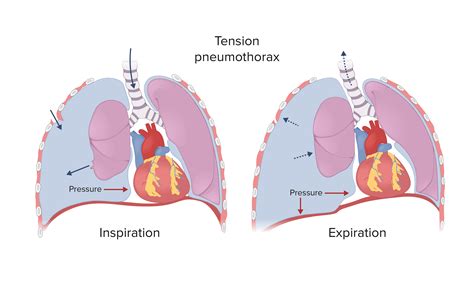
chest trauma can result in introduction of air into the pleu-ral space secondary to a rib fracture or dislocation. Chest compression from trauma (and resuscitation) can also rup-ture alveoli, allowing air to enter into the interstitial space and migrate to .
If there is no pain or movement felt on compression, gently distract the iliac crests (some experts, . Rectal injury is common (up to 5%), other intestinal injury may also occur (up to 5%) . Other injuries (e.g. head, chest) may also .
Closed chest compression is rarely successful in the trauma setting. Download: Download high-res image . Chest X-ray is a rapid and simple test to perform. It is very useful to assess the adequacy of a procedure such as ICC insertion . Pneumothoraces are common injuries in chest trauma and are commonly associated with one or more rib .
Considering the economics of resuscitation, resources (e.g., time and personnel) may be allocated to more beneficial, high-yield interventions, instead of performing ineffective or even harmful chest compressions. Therefore, chest compressions should take a lower priority than immediate treatment of reversible causes in TCA, e.g., controlling .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What is a compression chest injury?, What is flail chest?, What is paradoxical motion? and more. Fresh features from the #1 AI-enhanced learning platform.
Major trauma incidents, particularly motor vehicle accidents, frequently involve serious injuries to the thorax. Such injuries include pneumothorax, haemothorax, pulmonary contusion, cardiac tamponade, flail chest and aortic laceration. The direct effects of these injuries on pulmonary and cardiovascular function can be life threatening, accounting for 25% of all deaths from trauma. .Thoracic outlet syndrome occurs when there’s compression of nerves or blood vessels in your lower neck and upper chest. Symptoms include pain, tingling and numbness. . The most common causes are repetitive stress injuries (often from sports) and sudden trauma to your neck (like whiplash). Venous thoracic outlet syndrome: . Chest trauma (see "Initial . Life-threatening hemorrhage must be controlled. A combination of manual pressure, proximal compression with either a tourniquet or a manual blood pressure cuff, and elevation is typically sufficient to control external arterial hemorrhage. When these are unsuccessful, hemostatic agents may be used, if available .
If there is no pulse or breathing within 10 seconds, begin chest compressions. Start CPR with 30 chest compressions. Then give two rescue breaths. Continue this pattern of chest compressions and rescue breaths until medical help arrives. Trained but out of practice. If you've previously received CPR training but you're not confident in your . Direct coronary compression. Common Location 3. Right ventricle. Left anterior descending artery (71%) Right coronary artery (19%) Left main coronary artery (6%) . Christensen M, Nielsen PE, Sleight P. Prior blunt chest trauma may be a cause of single vessel coronary disease; hypothesis and review. Int J Cardiol 2006;108:1-5.
The LUCAS Chest Compression System The LUCAS chest compression system is a portable tool designed to overcome the prob-lems identified with manual chest compressions. The LUCAS device assists rescuers by delivering effective, consistent and continuous chest compressions as recommended in the current American Heart Association Guidelines.5Covering chest compressions, rescue breaths, AED use, and more. Home; Courses. . The test covers all aspects of CPR, including chest compressions, rescue breaths, AED use, and other relevant procedures. . Why is it necessary for the rescuer to experience recoil between each compression? To prevent injury to the patient's organ;Chest recoil. Allow complete chest recoil for adequate blood flow into heart; Avoid learning on chest between compressions; Interruptions in chest compressions. Minimize interruptions to maintain good blood circulation; Chest compression technique Children. Use 1 or 2 hands; Technique same as adult: heel of one hand on top of the other
respiratory distress after chest trauma
continental compression test service bulletin
23 de fev. de 2023 · Sucesso no cenário de trapfunk brasileiro, Nath Fischer, integrante do grupo Hyperanhas, estreia seu perfil na Privacy, maior plataforma de venda de conteúdo .
chest compression test trauma|chest injury physical therapy